System Suitability Criteria
Controls
Upper and lower limits can be set for the mean or geometric mean of:
a) All control samples
-
By groups if present e.g. high, low
Reference standard
Goodness of fit of the model
-
If there is more than one replicate at each dose: lack of fit error can be compared with pure error via an F test.
-
The level (critical p value) can be chosen by the user.
-
If there is only 1 replicate, there is no Goodness of fit estimation.
Parameter values
-
-
-
-
The confidence level for the each interval can be chosen by the user (no default setting).
Statistical significance of dose response 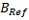
-
via a one-sample t test comparing 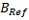 with zero.
with zero.
-
The level (critical p value) can be chosen by the user
-
Combination of parameter values
-
Limits for the values of the following can be set.
-
The range (difference between asymptotes): |

-
The midpoint (ED50) of the 5PL : 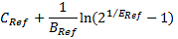
-
The amount of asymmetry: Ln(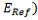
-
Equivalence limits for the following can be set:
-
Range for the confidence intervals for (no default setting)
-
The range (difference between asymptotes): |

-
The midpoint (ED50) of the 5PL : 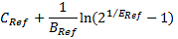
-
The amount of asymmetry: Ln(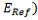
-
The confidence level for the each interval can be chosen by the user (no default setting).
Variability of data
-
An upper limit for the variance, σ2Ref, Mean square error (MSE), can be set.
-
An upper limit for σRef the root mean square error (RMSE) can be set.
Quality Control
Goodness of fit of the model
-
If there is more than one replicate at each dose: lack of fit error can be compared with pure error via an F test.
-
The level (critical p value) can be chosen by the user.
-
Statistical significance of 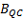
-
via a one-sample t test comparing 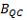 with zero.
with zero.
-
The level (critical p value) can be chosen by the user
-
Parallelism with reference standard
-
Ranges for combinations of QC and reference parameters can be chosen.
-
Difference between equivalent parameters:
-
(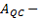

-
(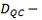
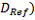
-
(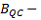
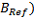
-
(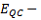
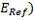
-
(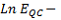
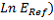
-
Normalised difference between asymptotes
-
-
-
Equivalence tests for combinations of QC and reference parameters.
-
Ranges for the confidence intervals (no default setting) for:
-
(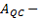

-
(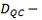
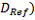
-
(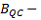
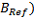
-
(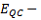
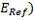
-
(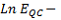
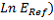
-
-
-
The confidence level for the each interval can be chosen by the user (no default setting).
-
Significance tests for lack of parallelism can be used:
-
F test comparing the unconstrained model with the parallel model.
-
The level (critical p value) can be chosen by the user.
-
-
χ2 test comparing the unconstrained model with the parallel model.
-
The level (critical p value) can be chosen by the user (no default value).
Relative potency of the QC sample, and its confidence interval
(For calculation of these parameters, see here.)-
-
-
Range for the confidence interval for RP (no default setting).
-
The confidence level can be chosen by the user (no default setting).
-
Precision: The ratio of upper confidence limit to lower confidence limit
-
The confidence level can be chosen by the user (no default setting).
-
The upper limit for the precision is chosen by the user