System Suitability Criteria
Controls
Upper and lower limits can be set for the mean or geometric mean of:
-
-
By groups if present e.g. high, low
Reference standard
Goodness of fit of the model
, or ‘linearity’
Quality Control
Goodness of fit of the model
, or ‘linearity’
-
If there is more than one replicate at each dose: lack of fit error can be compared with pure error via an F test.
-
The level (critical p value) can be chosen by the user.
-
-
A quadratic model can be fitted to the data and the significance of the quadratic term tested via a t test.
-
The level (critical p value) can be chosen by the user.
-
-
The R2 for the regression can be calculated.
-
The minimum value must be chosen by the user (no default setting).
Statistical significance of the slope
, BQC via a one-sample t test comparing the slope with zero.
-
The level (critical p value) can be chosen by the user
-
-
The sign of the slope must be stated (positive or negative).
Parallelism with reference standard
-
Ranges for combinations of QC and reference slope parameters can be chosen.
-
Difference between slopes: 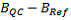
-
Ratio of slopes: 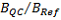
-
Normalised slope difference: 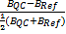
-
Equivalence tests for combinations of QC and reference slope parameters.
-
Ranges for the confidence intervals (no default setting) for:
-
Difference between slopes: 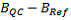
-
Ratio of slopes: 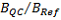
-
Normalised slope difference: 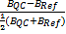
-
The confidence level for the each interval can be chosen by the user (no default setting).
-
Significance tests for lack of parallelism can be used:
-
F test comparing the model with separate slopes with the parallel model.
-
The level (critical P value) can be chosen by the user.
-
-
χ2 test comparing the model with separate slopes with the parallel model.
-
The level (critical P value) can be chosen by the user (no default setting).
Relative potency of the QC sample
, and its confidence interval (For calculation of these parameters, see 3.1.5 below)
a) Allowed range for RP
b) Equivalence test for RP
-
Range for the confidence interval for RP (no default setting).
-
The confidence level can be chosen by the user (no default setting).
c) Precision: The ratio of upper confidence limit to lower confidence limit
-
The confidence level can be chosen by the user (no default setting).
-
The upper limit for the precision is chosen by the user